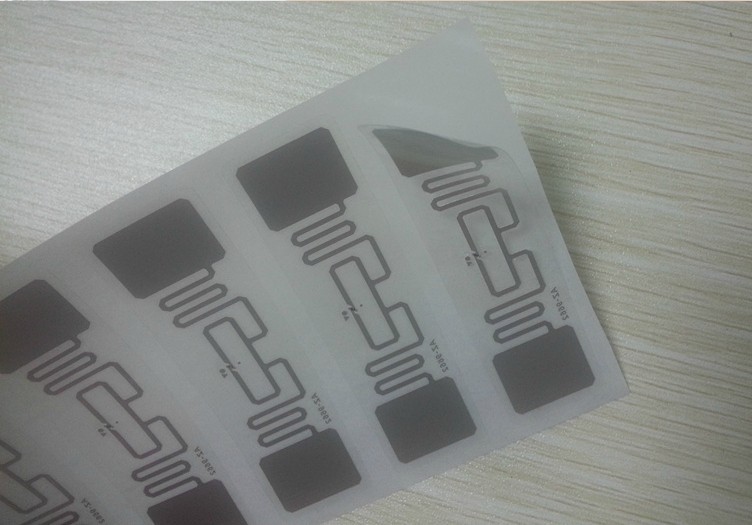
Imagine a future in which your every belonging is marked with a unique number identifiable with the swipe of a scanner; where your refrigerator keeps track of its contents; where the location of your car is always pinpoint-able; and where signal-emitting microchips storing personal information are implanted beneath your skin or embedded in your inner organs. RFID is similar to barcode systems in which data, such as a price, is accessed when the barcode is read. The main difference is that the barcode must come in direct contact to an optical reader and the dry inlay RFID tag can transmit to the reader via radio waves and does not have to be in direct contact. The RFID technology can improve performance and efficiency but is expensive to startup.
This gives RFID tags a distinct advantage over optically read items, such as barcodes, which would be useless under similar conditions. RFID tags consist of a microchip connected to an antenna, which is constructed of a small coil of wires. A passive RFID tag draws its power from this magnetic field, which powers the circuits in the microchip allowing it to transmit data back to the reader. The most expensive read/write, active RFID transponders may have microchips with a memory capacity of up to one megabyte (1,000,000 characters).
The main difference is that the barcode must come in direct contact to an optical scanner/reader and the dry inlay rfid tag can transmit to the reader via radio waves and does not have to be in direct contact. Testing of RFID antennae is usually performed with ohmmeters, milliohm meters, RF network analyzers, impedance-measuring equipment, and others. CXJ RFID tags can be manufactured in several different shapes and sizes depending on the type of application in which they will be used.
This gives RFID tags a distinct advantage over optically read items, such as barcodes, which would be useless under similar conditions. Quality control is a necessity because groups of manufactured inlays may have experienced some damage before they reach the printer or converter. The chips in the inlays can also be damaged during the printing or converting process, which renders the RFID tag useless. When RFID antennae are manufactured, they are usually tested with ohmmeters, milliohm meters, RF network analyzers, and impedance-measuring equipment.
Some printers purchase dry inlay that are already manufactured and then incorporate them into their printed products. Label printing is one of the fastest growing segments of the printing industry using RFID technology. Equipment is available that is able to encode a separate RFID inlay and then bond it to the substrate after the label has been printed. The printers can read, write, and print labels that have an embedded RFID transponder.